Đăng nhập để tiếp tục
Phương pháp 1: Đăng ký vào website
Nếu chưa có tài khoản, hãy đăng ký để trải nghiệm dịch vụ.
Phương pháp 2: Đăng nhập vào website
Khi đăng nhập, bạn sẽ có trải nghiệm dịch vụ tốt hơn.
🎓 Tư vấn lộ trình
Để lại thông tin để được tư vấn miễn phí và trải nghiệm lộ trình học phù hợp nhất!
Tiến độ
LESSON
MASTERING RHETORICAL SYNTHESIS QUESTIONS
Table of Contents
Introduction
- Mastering Rhetorical Synthesis Questions
- The GOAL Method for Rhetorical Synthesis
Core Concepts
- Understanding Different Goal Types
- Recognizing Information Relationships
- Strategic Selection Principles
Practice Questions
- Practice Question 1 - Chemistry
- Practice Question 2 - Physics
- Practice Question 3 - Physics/Technology
- Practice Question 4 - Biology
- Practice Question 5 - Ecology
- Practice Question 6 - Biology/Health
- Practice Question 7 - Evolution
Advanced Strategies
- Complex Rhetorical Goals
- Time Management and Test Strategy
Summary
- Mastering the GOAL Method
Bài nghe
Phát bài học
Audio Transcript
Welcome to your comprehensive guide for mastering SAT Rhetorical Synthesis questions! These unique questions represent one of the most innovative additions to the digital SAT, testing your ability to synthesize information from multiple bullet points to accomplish a specific rhetorical goal. Unlike traditional reading questions that ask you to analyze existing text, rhetorical synthesis questions provide you with a set of research notes and challenge you to determine which choice best uses that information to achieve a particular purpose. You'll encounter 2-4 of these questions per test, and they require a distinct approach that combines critical reading with strategic thinking. These questions simulate real-world research and writing tasks - imagine you're a student who has gathered notes on a topic and now needs to craft a sentence that effectively communicates a specific aspect of your research. The key to success lies not just in understanding the information provided, but in recognizing how different pieces of that information can be combined to accomplish the stated goal. Whether you're asked to emphasize a similarity, highlight a contrast, explain significance, or demonstrate a relationship, you'll need to think strategically about which facts to include and how to present them. Let's dive into the systematic approach that will help you excel at these sophisticated synthesis questions.
Key Points
- Tests ability to synthesize research notes for specific goals
- 2-4 questions per test in Reading and Writing section
- Simulates real-world research and writing scenarios
- Common goals: emphasize, explain, introduce, demonstrate
- Requires comprehension and strategic selection
- All answers grammatically correct - focus on effectiveness
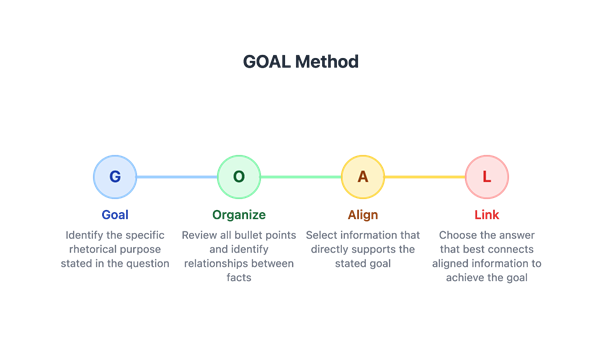
THE GOAL METHOD FOR RHETORICAL SYNTHESIS
Bài nghe
Phát bài học
Audio Transcript
To master Rhetorical Synthesis questions, we'll use the GOAL method - a systematic four-step approach that ensures you select the most effective answer every time. G stands for Goal: Always start by identifying exactly what the question wants you to accomplish. This goal will be explicitly stated in the question stem, such as 'emphasize the significance,' 'explain the importance,' or 'highlight a similarity.' Understanding this goal is crucial because it determines which information from the notes is relevant and how it should be presented. O stands for Organize: Quickly review all the bullet points and mentally organize the information. Look for relationships between facts, identify which points are most relevant to the goal, and note any connections or contrasts. This step helps you see the full picture before making selections. A stands for Align: Determine which specific pieces of information directly align with and support the stated goal. Not all bullet points will be relevant - focus only on those that help accomplish what the question asks. Consider how different combinations of facts might work together. L stands for Link: Evaluate each answer choice to see which one best links the aligned information to accomplish the goal. The correct answer will not only use accurate information but will present it in a way that most effectively achieves the stated purpose. Remember, all choices will be grammatically correct and may use accurate information - your job is to find the one that best accomplishes the specific rhetorical goal. Let's see how this method works with real SAT-style questions.
Key Points
- G - Goal: Identify the specific rhetorical purpose
- O - Organize: Review notes and identify relationships
- A - Align: Select information supporting the goal
- L - Link: Choose answer that best achieves purpose
UNDERSTANDING DIFFERENT GOAL TYPES
Common Rhetorical Goals in SAT Questions
Emphasis Goals
"Emphasize the significance/importance of..."
These goals require you to show why something matters. You're not just stating facts but demonstrating impact, relevance, or consequence. Look for:
- Cause-effect relationships
- Broader implications
- Connections to larger principles
- Why something is notable or exceptional
Example Pattern: Position/characteristic → Why it matters
Explanation Goals
"Explain how/why..."
These goals ask you to clarify mechanisms, processes, or reasons. You need to show the logical connection between elements. Look for:
- Step-by-step processes
- Causal chains
- Underlying principles
- How something works or functions
Example Pattern: Principle/Theory → Application/Effect
Introduction Goals
"Introduce [topic] to [audience]"
These goals require context-setting and clear definition. Start broad, then narrow to specifics. Consider:
- What the audience needs to know first
- Essential background information
- Clear definitions or descriptions
- Logical progression from general to specific
Example Pattern: Context → Definition → Significance
Demonstration Goals
"Demonstrate the relationship between..."
These goals focus on connections. You must show how elements interact or relate. Look for:
- Direct connections
- Mutual influences
- Comparative relationships
- How one element affects another
Example Pattern: Element A + Element B → Their connection
Bài nghe
Phát bài học
Audio Transcript
Understanding different goal types is crucial for success on rhetorical synthesis questions. Each goal type requires a distinct approach and selection strategy. Emphasis goals ask you to show significance or importance. You're not just stating facts but demonstrating why something matters. Look for cause-effect relationships, broader implications, and connections to larger principles. The pattern often moves from a specific position or characteristic to explaining why it's notable. Explanation goals require you to clarify how or why something happens. Show mechanisms, processes, or logical connections between elements. Look for step-by-step progressions, causal chains, and underlying principles that make something work. The pattern typically moves from principle to application. Introduction goals need careful audience consideration. Start with necessary context, provide clear definitions, then show significance. Think about what someone unfamiliar with the topic needs to know first. The pattern progresses from general context to specific details. Demonstration goals focus on relationships between elements. Show how things connect, interact, or influence each other. Look for direct connections, mutual influences, and comparative relationships. The pattern links multiple elements to reveal their connection. Recognizing these patterns helps you quickly identify which information to select and how to evaluate answer choices. Each goal type has its own rhetorical demands.
Key Points
- Emphasis: Show why something matters or has impact
- Explanation: Clarify mechanisms, processes, or reasons
- Introduction: Provide context, then narrow to specifics
- Demonstration: Show connections between elements
- Each goal type requires different information selection
- Pattern recognition speeds up answer evaluation
RECOGNIZING INFORMATION RELATIONSHIPS
How Information Relates in Research Notes
Types of Information Relationships
1. Hierarchical Relationships
- General → Specific: Broad concepts followed by examples
- Category → Instance: Types followed by specific cases
- Principle → Application: Theory followed by practice
2. Causal Relationships
- Cause → Effect: One fact leads to another
- Problem → Solution: Challenge followed by response
- Discovery → Impact: Finding followed by consequences
3. Comparative Relationships
- Similarity: Shared characteristics or patterns
- Difference: Contrasting features or approaches
- Evolution: Changes over time or development
4. Supporting Relationships
- Claim → Evidence: Statement followed by proof
- Definition → Characteristic: What something is and its features
- Function → Significance: What it does and why it matters
Reading Research Notes Strategically
First Pass: Identify the Topic
- What is the main subject?
- What aspect is being examined?
Second Pass: Map Relationships
- How do facts connect?
- Which facts support each other?
- What patterns emerge?
Third Pass: Match to Goal
- Which relationships serve the stated goal?
- What combination tells the right story?
Common Patterns in SAT Notes
- Scientific Pattern: Discovery → Properties → Applications → Significance
- Historical Pattern: Context → Event → Impact → Legacy
- Analytical Pattern: Observation → Analysis → Conclusion → Implications
Bài nghe
Phát bài học
Audio Transcript
Recognizing how information relates within research notes is a critical skill for rhetorical synthesis success. The notes aren't random facts - they're carefully structured to contain multiple relationship types. Hierarchical relationships move from general to specific. You'll see broad concepts followed by specific examples, categories followed by instances, or principles followed by applications. These relationships help when goals require you to narrow focus or provide examples. Causal relationships show how one fact leads to another. Look for cause-effect chains, problems followed by solutions, or discoveries followed by their impacts. These relationships are crucial for explanation and significance goals. Comparative relationships highlight similarities, differences, or evolution over time. These help when demonstrating relationships or emphasizing contrasts between elements. Supporting relationships connect claims with evidence, definitions with characteristics, or functions with significance. These are essential for building comprehensive responses. When reading notes strategically, use three passes. First, identify the main topic and aspect being examined. Second, map how facts connect and support each other. Third, match these relationships to your goal. Common patterns emerge: scientific notes often follow discovery to significance, historical notes move from context to legacy, and analytical notes progress from observation to implications. Understanding these relationships transforms scattered facts into coherent narratives aligned with your rhetorical goal.
Key Points
- Hierarchical: General to specific relationships
- Causal: Cause-effect and problem-solution chains
- Comparative: Similarities, differences, evolution
- Supporting: Claims with evidence, definitions with features
- Use three passes: Topic, Relationships, Goal matching
- Recognize patterns: Scientific, Historical, Analytical
STRATEGIC SELECTION PRINCIPLES
Principles for Selecting Information Effectively
The Relevance Hierarchy
Essential Information (Must Include)
- Directly addresses the stated goal
- Core facts without which the response fails
- Key terms that define the topic
Supporting Information (Should Include)
- Strengthens the main point
- Provides necessary context
- Clarifies relationships
Peripheral Information (Usually Exclude)
- Interesting but unrelated to goal
- Too specific for broad goals
- Too general for specific goals
Quality Over Quantity
Effective Synthesis Is:
- Focused: Every fact serves the goal
- Precise: Right level of detail for purpose
- Complete: Includes all necessary elements
- Clear: Logical flow from start to finish
Avoid These Traps:
- Including facts just because they're interesting
- Using all available information
- Missing key connections between facts
- Choosing the longest answer
Matching Scope to Goal
Broad Goals Need:
- Overview information
- General principles
- Wide-ranging implications
Narrow Goals Need:
- Specific examples
- Particular details
- Focused applications
The Integration Test
Ask yourself:
- Does this choice integrate facts smoothly?
- Do the selected facts work together?
- Is the progression logical?
- Does it fully accomplish the goal?
If any answer is no, reconsider your choice.
Bài nghe
Phát bài học
Audio Transcript
Strategic selection of information separates good responses from great ones in rhetorical synthesis. Not all facts are equal - you must prioritize based on relevance to your goal. Essential information directly addresses the stated goal and includes core facts without which your response fails. This might be key definitions, central relationships, or primary characteristics. Always include these first. Supporting information strengthens your main point by providing context or clarifying relationships. Include this when it enhances understanding without overwhelming the response. Peripheral information may be interesting but doesn't serve your goal - exclude it regardless of accuracy. Remember quality over quantity. Effective synthesis is focused with every fact serving the goal, precise with the right level of detail, complete with all necessary elements, and clear with logical flow. Avoid common traps like including facts just because they're interesting or choosing the longest answer. More isn't always better. Match your scope to the goal. Broad goals need overview information and general principles, while narrow goals require specific examples and focused details. Don't use specific examples for broad introductions or general statements for detailed demonstrations. Apply the integration test: Does the choice integrate facts smoothly? Do they work together logically? Is the progression clear? Does it fully accomplish the goal? If any answer is no, reconsider. The best synthesis seamlessly weaves selected facts into a coherent response.
Key Points
- Prioritize essential facts that directly serve the goal
- Include supporting context when it enhances clarity
- Exclude peripheral information regardless of interest
- Quality over quantity - more facts isn't always better
- Match scope: broad goals need overviews, narrow need specifics
- Test integration: smooth, logical, complete goal accomplishment
PRACTICE QUESTION 1 - CHEMISTRY
While researching a topic, a student has taken the
following notes:
• The periodic table organizes elements by increasing
atomic number.
• Each row on the periodic table is called a period.
• Elements in the same column, or group, share similar
chemical properties.
•
The element helium (He) is in the top-right corner of the periodic table.
•
Helium is known for its low reactivity due to a full outer electron shell.
· The student wants to emphasize the significance of helium's position on the periodic table. G: Identifies the specific goal - showing why position matters
· • The element helium (He) is in the top-right corner of the periodic table. O: Key information about helium's position
· • Helium is known for its low reactivity due to a full outer electron shell. O: Key information about helium's properties
· Located in the top-right corner of the periodic table, helium's position highlights its unique low reactivity and full outer electron shell. L: Successfully links position to properties, emphasizing significance
Giải thích:
Choice D is correct because it directly links helium's position on the periodic table to its chemical properties, specifically its low reactivity and full outer electron shell, effectively emphasizing the significance of its placement.
Bài nghe
Phát bài học
Audio Transcript
Let's apply the GOAL method to our first rhetorical synthesis question about helium and the periodic table. Goal: The question explicitly asks us to 'emphasize the significance of helium's position on the periodic table.' This means we need to show why helium's location matters - not just state where it is, but explain what that position tells us about the element. Organize: Looking at our bullet points, we have general information about the periodic table's organization, specific information about helium's location (top-right corner), and crucial information about helium's properties (low reactivity, full outer electron shell). The key insight is connecting position to properties. Align: For emphasizing significance, we need the bullet points about helium's specific position (top-right corner) and its distinctive properties (low reactivity, full outer electron shell). The significance lies in how position reflects properties on the periodic table. Link: Now let's evaluate each choice. Choice A only provides general periodic table information without mentioning helium at all - this clearly fails our goal. Choice B mentions that elements in the same column share properties and references helium, but doesn't specify helium's position or what makes it significant. Choice C mentions helium's position but vaguely refers to 'unique properties' without explaining what they are or why the position is significant. Choice D perfectly accomplishes our goal by explicitly connecting helium's top-right position to its specific properties - low reactivity and full outer electron shell. This choice shows that helium's position isn't arbitrary but reflects its fundamental chemical characteristics. The word 'highlights' effectively emphasizes the significance we're asked to convey.
Key Points
- G - Goal: Emphasize why helium's position is significant
- O - Organize: Connect position to chemical properties
- A - Align: Select helium's location and characteristics
- L - Link: Choice D best shows position reflects properties
PRACTICE QUESTION 2 - PHYSICS
While researching a topic, a student has taken the
following notes:
•
Newton's third law of motion states that for every action, there is an equal and
opposite reaction.
• This law explains the principle of conservation of
momentum in collisions.
• In a closed system, the total momentum before and
after a collision is the same.
• Momentum is a product of an object's mass and
velocity.
•
This law is crucial for understanding the dynamics of space travel and rocket
launches.
· The student wants to present the significance of Newton's third law of motion in understanding space travel. G: Clear goal focusing on space travel applications
· • Newton's third law of motion states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. O: Core principle of the law
· • This law is crucial for understanding the dynamics of space travel and rocket launches. O: Direct connection to space travel
· By elucidating how action and reaction forces work, Newton's third law of motion underpins the mechanics of rocket launches and space travel dynamics. L: Effectively links the principle to its significance in space travel
Giải thích:
Choice B is correct because it specifically relates Newton's third law of motion to its application in understanding the fundamental principles of rocket launches and space travel, thereby emphasizing its significance in this context.
Bài nghe
Phát bài học
Audio Transcript
Now let's tackle a physics question about Newton's third law and space travel using our GOAL method. Goal: We need to 'present the significance of Newton's third law of motion in understanding space travel.' Notice the specific focus - not just explaining the law, but showing why it matters for space travel specifically. This requires connecting the theoretical principle to its practical application. Organize: Our bullet points include the basic statement of Newton's third law (action-reaction), its connection to momentum conservation, the definition of momentum, and crucially, a direct statement about its importance for space travel and rocket launches. We need to strategically combine these elements. Align: The most relevant information includes the basic principle of action-reaction forces and the explicit connection to space travel and rocket launches from the last bullet point. While momentum is related, it's not the most direct path to explaining space travel applications. Link: Examining our choices - Choice A discusses momentum but makes no connection to space travel, failing our goal entirely. Choice C focuses on momentum conservation in collisions, which also misses the space travel connection. Choice D states the law generally but doesn't relate it to space travel at all. Choice B brilliantly accomplishes our goal by explaining how the action-reaction principle ('how action and reaction forces work') directly 'underpins the mechanics of rocket launches and space travel dynamics.' The word 'underpins' effectively conveys significance by showing the law as foundational to understanding space travel. The choice uses sophisticated vocabulary ('elucidating') and makes the connection explicit rather than leaving it implied.
Key Points
- G - Goal: Show Newton's third law's significance for space travel
- O - Organize: Connect action-reaction to rocket applications
- A - Align: Focus on law's statement and space travel relevance
- L - Link: Choice B shows law 'underpins' space mechanics
PRACTICE QUESTION 3 - PHYSICS/TECHNOLOGY
While researching a topic, a student has taken the
following notes:
•
The theory of relativity introduced by Einstein revolutionized the
understanding of time, space, and gravity.
• It asserts that the laws of physics are the same for
all non-accelerating observers.
• According to relativity, time can slow down or speed
up, depending on how fast you are moving relative to something else.
• The famous equation E=mc² shows the equivalence of
mass and energy.
•
This theory has implications for the development of modern GPS technology.
· The student wants to explain the impact of the theory of relativity on modern technology. G: Goal requires showing how theory influenced technology
· • The theory of relativity introduced by Einstein revolutionized the understanding of time, space, and gravity. O: Revolutionary nature of the theory
· • This theory has implications for the development of modern GPS technology. O: Specific technological application
· The theory of relativity not only transformed our comprehension of time and space but also laid the groundwork for the development of technologies like GPS. L: Connects theoretical transformation to technological development
Giải thích:
Choice C is correct because it directly connects the theoretical advancements introduced by Einstein's theory of relativity to their practical application in modern technologies such as GPS, effectively highlighting the theory's impact.
Bài nghe
Phát bài học
Audio Transcript
This question asks us to bridge theoretical physics with practical technology - let's apply our GOAL method systematically. Goal: We must 'explain the impact of the theory of relativity on modern technology.' The key word here is 'impact' - we need to show not just what the theory says, but how it has influenced technological development. This requires connecting abstract concepts to concrete applications. Organize: Our notes cover the revolutionary nature of relativity, its core principles about physics laws and time dilation, the famous E=mc² equation, and importantly, a specific technological application - GPS. We need to show the journey from theory to technology. Align: The most relevant information includes the theory's revolutionary nature (showing it was significant enough to have impact) and the specific mention of GPS technology. While time dilation is part of how GPS works, we need to focus on the broader impact story. Link: Let's analyze each choice. Choice A describes the theory but makes no mention of technology or impact - it stops at the theoretical level. Choice B focuses solely on E=mc² without connecting to technology. Choice D mentions GPS but only addresses one specific principle (time dilation) rather than explaining the broader impact. Choice C excellently accomplishes our goal by presenting a two-part narrative: first, it acknowledges how relativity 'transformed our comprehension of time and space' (showing its revolutionary nature), then it directly states it 'laid the groundwork for the development of technologies like GPS.' The phrase 'laid the groundwork' effectively conveys impact by showing relativity as foundational to modern technology. The word 'technologies' (plural) with 'like GPS' suggests GPS is just one example of a broader technological impact, which strengthens the response.
Key Points
- G - Goal: Explain how relativity impacted modern technology
- O - Organize: Link revolutionary theory to tech applications
- A - Align: Focus on theory's significance and GPS mention
- L - Link: Choice C shows impact through transformation to development
PRACTICE QUESTION 4 - BIOLOGY
While researching a topic, a student has taken the
following notes:
• DNA replication is a process by which a cell
duplicates its DNA before cell division.
• Enzymes play a critical role in unwinding the DNA
double helix and synthesizing new strands.
•
The replication process ensures genetic information is accurately passed to daughter
cells.
• Mutations can occur if there is an error in the
replication process.
•
DNA replication is semi-conservative, meaning each new DNA molecule contains one
original strand and one new strand.
· The student wants to emphasize the accuracy and importance of the DNA replication process. G: Dual goal requiring both precision and significance
· • The replication process ensures genetic information is accurately passed to daughter cells. O: Key fact about accuracy
· • DNA replication is semi-conservative, meaning each new DNA molecule contains one original strand and one new strand. O: Mechanism that ensures accuracy
· By accurately duplicating genetic information for daughter cells, DNA replication's semi-conservative process plays a crucial role in heredity and mutation prevention. L: Integrates accuracy, mechanism, and importance effectively
Giải thích:
Choice B is correct because it succinctly captures the essence of DNA replication, highlighting its precision and significance in passing genetic information accurately to daughter cells, as well as its role in minimizing mutations, which underscores the importance of the process.
Bài nghe
Phát bài học
Audio Transcript
This biology question requires us to emphasize two linked concepts - accuracy and importance. Let's work through our GOAL method carefully. Goal: We need to 'emphasize the accuracy and importance of the DNA replication process.' This dual goal means we must highlight both how precise the process is and why that precision matters for life. We're looking for a choice that addresses both aspects effectively. Organize: Our bullet points cover the mechanism of replication, enzyme roles, the accuracy of genetic information transfer, potential for mutations (showing what happens when accuracy fails), and the semi-conservative nature. The relationship between accuracy and importance is key - the process is important precisely because it must be accurate. Align: The most relevant information includes the accurate passing of genetic information to daughter cells (showing both accuracy and importance), the semi-conservative nature (a mechanism ensuring accuracy), and the mutation possibility (highlighting why accuracy matters). Link: Analyzing our options - Choice A merely describes the mechanical process without addressing accuracy or importance. Choice C focuses on when things go wrong (mutations) rather than emphasizing the normal accuracy and importance. Choice D explains semi-conservative replication but doesn't connect this to accuracy or importance. Choice B masterfully accomplishes both parts of our goal. It emphasizes accuracy by using the adverb 'accurately' and linking it to the semi-conservative process. It emphasizes importance through multiple elements: 'plays a crucial role' (explicit importance), 'heredity' (showing long-term significance), and 'mutation prevention' (showing what accuracy prevents). The choice presents DNA replication as both remarkably precise and fundamentally important to life's continuity. The sophisticated structure connects mechanism (semi-conservative process) to function (accurate duplication) to significance (heredity and mutation prevention).
Key Points
- G - Goal: Emphasize both accuracy and importance
- O - Organize: Connect accurate transfer to biological significance
- A - Align: Focus on precision and role in heredity
- L - Link: Choice B combines accuracy with crucial role
PRACTICE QUESTION 5 - ECOLOGY
While researching a topic, a student has taken the
following notes:
• Ecosystems are communities of living organisms
interacting with their physical environment.
• Biodiversity within ecosystems provides resilience
against environmental changes.
•
Keystone species play a critical role in maintaining the structure of an ecological
community.
•
The removal of a keystone species can lead to significant changes in
ecosystem composition and function.
• Conservation efforts aim to protect biodiversity and
the stability of ecosystems.
· The student wants to explain the importance of keystone species in ecosystems. G: Goal focuses on explaining why keystone species matter
· • Keystone species play a critical role in maintaining the structure of an ecological community. O: Positive role of keystone species
· • The removal of a keystone species can lead to significant changes in ecosystem composition and function. O: Negative consequences of removal
· Keystone species are pivotal in maintaining ecological community structures, with their removal potentially disrupting ecosystem composition and function. L: Combines role and consequences to explain importance
Giải thích:
Choice D is correct because it directly addresses the critical role of keystone species in sustaining the structure of ecological communities, emphasizing the significant impact their removal can have on ecosystem composition and function, which aligns with the student's goal to explain their importance.
Bài nghe
Phát bài học
Audio Transcript
For this ecology question about keystone species, we need to apply our GOAL method to highlight a specific ecological concept. Goal: We must 'explain the importance of keystone species in ecosystems.' This requires us to go beyond just defining keystone species - we need to show why they matter to ecosystem health and stability. The explanation should make clear their unique and critical role. Organize: Our notes provide a hierarchical understanding: general ecosystem definition, biodiversity's role in resilience, the specific role of keystone species, consequences of their removal, and conservation goals. The keystone species information is embedded within this broader context. Align: The directly relevant information is found in two bullets - keystone species playing a critical role in maintaining ecological structure, and the significant changes that occur when they're removed. These two points together demonstrate importance through both positive presence and negative absence. Link: Evaluating our choices - Choice A discusses ecosystems and biodiversity broadly without mentioning keystone species at all. Choice B focuses on biodiversity's resilience role but ignores keystone species entirely. Choice C addresses conservation efforts generally without explaining keystone species' importance. Choice D perfectly accomplishes our goal by combining both relevant pieces of information. It states that keystone species are 'pivotal' (showing importance) in 'maintaining ecological community structures' (explaining their role), and then strengthens this by explaining consequences - 'their removal potentially disrupting ecosystem composition and function.' This cause-and-effect structure effectively explains importance by showing what keystone species do and what happens without them. The word 'pivotal' is particularly effective, as it conveys that keystone species are central points around which ecosystems revolve, much like a pivot point in mechanics.
Key Points
- G - Goal: Explain why keystone species are important
- O - Organize: Identify role and removal consequences
- A - Align: Select function and impact information
- L - Link: Choice D explains importance through role and effects
PRACTICE QUESTION 6 - BIOLOGY/HEALTH
While researching a topic, a student has taken the
following notes:
• The human circulatory system is responsible for
transporting nutrients and oxygen to cells.
• It consists of the heart, blood, and blood vessels
such as arteries, veins, and capillaries.
•
The heart functions as a pump to circulate the blood throughout the body.
• Blood pressure is the force that blood exerts against
the walls of blood vessels.
•
Maintaining a healthy circulatory system is crucial for overall health and well-being.
· The student wants to present the significance of the heart in the human circulatory system. G: Goal requires showing the heart's special importance
· • The heart functions as a pump to circulate the blood throughout the body. O: Heart's unique function
· • Maintaining a healthy circulatory system is crucial for overall health and well-being. O: System's health importance
· As the pump of the circulatory system, the heart plays a pivotal role in circulating blood throughout the body, underscoring its significance for health. L: Emphasizes heart's unique pumping role and health significance
Giải thích:
Choice C is correct because it specifically highlights the heart's
role as the central pump of the circulatory system, emphasizing its critical
function in circulating blood and thus directly addressing the significance
of the heart within the system.
Bài nghe
Phát bài học
Audio Transcript
This question about the heart requires us to highlight one component's significance within a larger system. Let's apply GOAL methodically. Goal: We need to 'present the significance of the heart in the human circulatory system.' This means we must show not just what the heart does, but why it's particularly important compared to other components. We're emphasizing the heart's unique and crucial role. Organize: Our notes describe the circulatory system's overall function, its components, the heart's specific role as a pump, blood pressure, and the importance of circulatory health. The heart is presented as one component among several, but with a unique function. Align: The most relevant information includes the heart's role as a pump and how this enables blood circulation throughout the body. We should also connect this to the overall health importance mentioned in the last bullet. The heart's pumping function is what makes the entire system work. Link: Examining our choices - Choice A lists the heart as just one component among others without emphasizing its particular significance. Choice B focuses on blood pressure without mentioning the heart at all. Choice D mentions the heart but groups it equally with blood and vessels, failing to highlight its unique significance. Choice C excellently accomplishes our goal through several strategies. First, it identifies the heart's unique role 'as the pump of the circulatory system' - showing it's not just another component but the driving force. The phrase 'pivotal role' emphasizes significance. It then explains what this means functionally - 'circulating blood throughout the body.' Finally, it connects to health significance with 'underscoring its significance for health.' The choice presents the heart as the essential engine of the circulatory system, without which the entire system would fail. The progressive structure - role, function, significance - builds a complete argument for the heart's importance.
Key Points
- G - Goal: Present heart's particular significance
- O - Organize: Identify heart's unique pumping role
- A - Align: Focus on pump function and health connection
- L - Link: Choice C emphasizes pivotal role and significance
PRACTICE QUESTION 7 - EVOLUTION
While researching a topic, a student has taken the
following notes:
• Evolution is the process by which species change over
time through natural selection.
•
Natural selection acts on genetic variations within populations.
• Mutations introduce new genetic variations into a
population's gene pool.
•
Over time, advantageous traits become more common in the population.
• Evolutionary theory explains the diversity of life
forms on Earth.
· The student wants to emphasize the role of natural selection in evolution. G: Goal requires highlighting natural selection's central function
· • Natural selection acts on genetic variations within populations. O: Natural selection's mechanism
· • Over time, advantageous traits become more common in the population. O: Natural selection's effects
· Natural selection, by acting on genetic variations, is a fundamental process in evolution, leading to the development of advantageous traits in populations over time. L: Makes natural selection the subject and shows its driving role
Giải thích:
Choice A is correct because it clearly articulates the mechanism of natural selection and its pivotal role in the evolutionary process. It explains how natural selection acts on genetic variations to favor the development and prevalence of advantageous traits within a population, thereby driving evolution.
Bài nghe
Phát bài học
Audio Transcript
Our final practice question addresses a fundamental biological concept - let's use GOAL to emphasize natural selection's role in evolution. Goal: We must 'emphasize the role of natural selection in evolution.' This requires showing not just that natural selection is part of evolution, but highlighting its central, driving function in the evolutionary process. We need to make natural selection the star of our explanation. Organize: Our notes present evolution as a process, with natural selection as its mechanism. We see the flow: mutations create variation, natural selection acts on this variation, advantageous traits increase over time, resulting in life's diversity. Natural selection is positioned as the key active force. Align: The most relevant information includes how natural selection acts on genetic variations and leads to advantageous traits becoming more common. This cause-and-effect relationship shows natural selection's active role in driving evolutionary change. We should focus on natural selection as the mechanism, not just a component. Link: Let's analyze each choice. Choice B focuses on mutations without mentioning natural selection at all - this completely misses our goal. Choice C mentions natural selection but relegates it to a subordinate clause ('which includes'), failing to emphasize its role. Choice D undermines natural selection's importance by calling it 'one of several mechanisms,' which actually de-emphasizes its role. Choice A perfectly accomplishes our goal through several techniques. It leads with 'Natural selection,' making it the subject and focus. It explains the mechanism - 'acting on genetic variations' - showing how natural selection works. It calls it 'a fundamental process,' emphasizing its essential role. Finally, it shows the outcome - 'leading to the development of advantageous traits in populations over time' - demonstrating natural selection's power to drive evolutionary change. The choice presents natural selection not as a passive component but as the active force shaping life's evolution. The clear causal chain from natural selection through genetic variation to advantageous traits effectively emphasizes its central role.
Key Points
- G - Goal: Emphasize natural selection's central role
- O - Organize: Connect natural selection to evolutionary outcomes
- A - Align: Focus on how selection acts on variations
- L - Link: Choice A emphasizes fundamental driving role
COMPLEX RHETORICAL GOALS
Mastering Complex Rhetorical Goals
Multi-Part Goals
Some questions contain compound goals requiring you to accomplish multiple objectives:
"Emphasize X AND explain Y"
- Must address both parts fully
- Balance coverage between elements
- Look for choices that integrate both smoothly
"Compare X and Y while highlighting Z"
- Primary goal: comparison
- Secondary goal: emphasis on specific aspect
- Successful choices accomplish both seamlessly
Audience-Aware Goals
"Introduce [topic] to [specific audience]"
- Consider audience's knowledge level
- Adjust technical language appropriately
- Include necessary context for understanding
Example: Introducing quantum physics to general readers requires different information than introducing it to physics students.
Process-Oriented Goals
"Demonstrate how X leads to Y"
- Show clear progression
- Include intermediate steps if necessary
- Make causal connections explicit
"Explain the development of X"
- Chronological or logical progression
- Key stages or turning points
- Factors driving change
Evaluative Goals
"Assess the impact of X on Y"
- Identify specific effects
- Consider multiple dimensions
- Make judgments about significance
Advanced Selection Strategies
- For Multi-Part Goals:
- Map which bullet points serve each part
- Ensure balanced coverage
- Avoid choices addressing only one aspect
- Prioritize accessibility over completeness
- Include definitions for technical terms
- Start with familiar concepts
- Identify beginning and end points
- Include key intermediate steps
- Show clear causal links
- Focus on concrete impacts
- Use specific examples
- Make significance clear
Bài nghe
Phát bài học
Audio Transcript
Complex rhetorical goals require sophisticated strategies beyond basic synthesis. Multi-part goals demand that you accomplish multiple objectives simultaneously. When facing 'emphasize X AND explain Y,' you must address both parts fully with balanced coverage. Look for choices that integrate both elements smoothly rather than handling them separately. Similarly, goals like 'compare X and Y while highlighting Z' have primary and secondary objectives that successful choices accomplish seamlessly. Audience-aware goals add another layer of complexity. Introducing a topic to a specific audience requires considering their knowledge level and adjusting technical language appropriately. Introducing quantum physics to general readers demands different information than introducing it to physics students. Include necessary context while maintaining accessibility. Process-oriented goals require showing clear progression. When demonstrating how X leads to Y, make causal connections explicit and include intermediate steps. Explaining development requires identifying key stages and factors driving change, whether chronologically or logically organized. Evaluative goals ask you to make judgments about significance. Assessing impact requires identifying specific effects across multiple dimensions and clearly conveying their importance. For multi-part goals, map which bullet points serve each part and ensure balanced coverage. For audience-aware goals, prioritize accessibility and start with familiar concepts. For process goals, identify clear beginning and end points with causal links. For evaluative goals, use concrete examples to demonstrate significance. Master these advanced strategies to handle any complex rhetorical challenge.
Key Points
- Multi-part goals require addressing all components fully
- Audience-aware goals need appropriate language and context
- Process goals show clear progression with causal links
- Evaluative goals assess impact and significance
- Map bullet points to different goal components
- Balance coverage and integrate elements smoothly
TIME MANAGEMENT AND TEST STRATEGY
Optimizing Performance on Test Day
Time Management Strategy
Recommended Timing: 45-60 seconds per question
- Read Goal (5-10 seconds)
- Circle or underline key directive words
- Identify all components of compound goals
- Mental note: emphasis? explanation? introduction?
- First pass: general topic understanding
- Second pass: identify relevant information
- Mark key facts mentally or physically
- Which bullet points serve the goal?
- What's the logical flow?
- Any obvious combinations?
- Eliminate choices missing key elements
- Compare remaining options carefully
- Select based on goal accomplishment
- Quick mental check: Does this fully accomplish the goal?
- Move on confidently
Speed-Building Techniques
Pattern Recognition
- Practice identifying goal types instantly
- Memorize common information relationships
- Develop instinct for relevant vs. peripheral facts
Efficient Elimination
- Choices missing goal elements = immediate elimination
- Off-topic information = immediate elimination
- Partial goal accomplishment = likely wrong
Trust Your Process
- First instinct often correct with good preparation
- Don't second-guess without clear reason
- Confidence comes from systematic approach
Common Time Wasters to Avoid
- Over-analyzing grammar - All choices are grammatically correct
- Comparing similar correct answers - Focus on goal accomplishment
- Re-reading all bullet points - Trust your initial scan
- Changing answers without clear reason - Stick with systematic choice
Test Day Mental Framework
Before Each Question:
- Take a breath, reset focus
- Remember: Goal drives everything
- Trust the GOAL method
If Stuck:
- Re-read the goal (not all the notes)
- Eliminate obvious wrong answers
- Choose the most goal-focused option
- Move on - don't let one question derail timing
Building Confidence:
- These questions reward systematic thinking
- Complexity is surface-level
- Your preparation has equipped you
- Trust the process, not perfection
Bài nghe
Phát bài học
Audio Transcript
Effective time management transforms rhetorical synthesis from a challenge into an opportunity for easy points. Aim for 45 to 60 seconds per question using this systematic approach. Start by reading the goal in 5 to 10 seconds, circling key directive words and identifying all components. Spend 10 to 15 seconds scanning bullet points - first pass for general understanding, second pass to identify relevant information. Take 5 to 10 seconds to plan your synthesis, determining which facts serve the goal and their logical flow. The bulk of your time, 20 to 25 seconds, goes to evaluating choices. Eliminate options missing key elements, compare remaining choices, and select based on goal accomplishment. Finally, spend 5 seconds confirming your selection with a quick mental check. Build speed through pattern recognition. Practice identifying goal types instantly and develop instinct for relevant versus peripheral facts. Eliminate efficiently - choices missing goal elements or containing off-topic information go immediately. Trust your process; your first instinct is often correct with good preparation. Avoid common time wasters like over-analyzing grammar (all choices are correct), comparing similar answers instead of focusing on goals, or changing answers without clear reason. On test day, reset focus before each question, remembering that goal drives everything. If stuck, re-read the goal, not all the notes. Choose the most goal-focused option and move on. These questions reward systematic thinking, and your preparation has equipped you for success.
Key Points
- 45-60 seconds per question optimal timing
- 5-10 seconds reading goal, 20-25 evaluating choices
- Circle key directive words in the goal
- Eliminate choices missing goal elements immediately
- Trust first instinct with systematic approach
- If stuck, re-read goal (not all notes) and move on
MASTERING THE GOAL METHOD
Summary
The GOAL Method: Your Key to Success
G - Goal: Identify the Specific Purpose
- Read carefully for directive words
- Note all components of compound goals
- Let the goal drive every decision
O - Organize: Survey and Map Information
- Identify topic and relationships
- Group related facts mentally
- Note which facts serve the goal
A - Align: Select Strategic Information
- Choose only goal-relevant facts
- Consider effective combinations
- Quality over quantity always
L - Link: Choose the Best Synthesis
- Evaluate goal accomplishment
- Assess rhetorical effectiveness
- Select clearest, most direct option
Bài nghe
Phát bài học
Audio Transcript
Congratulations on completing this comprehensive guide to SAT Rhetorical Synthesis questions! You've now mastered the GOAL method - your systematic approach to these unique questions that test real-world research and writing skills. Remember, these questions aren't about finding the most accurate statement or the most complete summary. They're about accomplishing a specific rhetorical goal using the information provided. Every time you encounter a rhetorical synthesis question, start with G - identify that goal precisely. What exactly does the question want you to accomplish? Then O - organize the information, looking for relationships and connections between the bullet points. Next A - align the most relevant facts with your goal, selecting only what directly helps accomplish the stated purpose. Finally L - link by choosing the answer that best synthesizes the aligned information to achieve the goal. The key insight is that rhetorical effectiveness trumps everything else. An answer can be completely accurate but still wrong if it doesn't accomplish the stated goal. Conversely, an answer doesn't need to use all available information - it just needs to use the right information in the right way. As you practice, you'll develop an instinct for recognizing which facts naturally work together to accomplish different types of goals. Whether you're emphasizing significance, explaining relationships, or introducing concepts, the GOAL method will guide you to the most effective synthesis. With consistent practice across all goal types and subject areas, you'll find these questions becoming some of the most straightforward on the test. Trust your preparation, apply the GOAL method systematically, and watch as these unique questions become a source of confidence rather than confusion. You're now equipped to handle any rhetorical synthesis challenge the SAT presents!
Key Points
- GOAL method ensures systematic success
- Goal drives every decision - read it first
- Synthesis creates connections, not just lists
- All answers grammatically correct - focus on effectiveness
- 45-60 seconds per question with practice
- Trust the process - complexity is only surface-level
Congratulations!
You've completed SAT Lesson: Rhetorical Synthesis. You can review the lesson again, or move on to the next lesson.